Medical grants are financial awards provided by various organizations, including government agencies, private foundations, and nonprofit institutions, to help individuals and healthcare facilities cover the costs associated with medical care. These grants serve as a vital resource for those who may not have adequate health insurance coverage or are facing significant out-of-pocket expenses.
In the realm of healthcare, understanding medical grants is paramount, as they serve as a lifeline for individuals and organizations grappling with the formidable financial challenges associated with medical expenses. From mounting doctor bills to the exorbitant costs of life-saving treatments, medical grants offer a glimmer of hope and crucial financial support when navigating the complex and often overwhelming world of healthcare financing.
The Significance of Medical Grants
Medical grants are financial awards provided by various entities, including government agencies, private foundations, and nonprofits, to help individuals and healthcare institutions cover the substantial costs linked to medical care. These grants, often regarded as financial lifelines, have a profound impact on the accessibility and quality of healthcare services, playing a pivotal role in:
- Reducing Financial Barriers: Medical expenses can pose a substantial burden, preventing individuals from seeking essential healthcare services. Medical grants help mitigate these barriers by covering expenses such as hospital stays, surgeries, medications, and specialized treatments.
- Advancing Medical Research: The realm of medical research relies heavily on grants to fund critical studies and clinical trials. These grants propel advancements in medical science, leading to innovative treatments, therapies, and a deeper understanding of various health conditions.
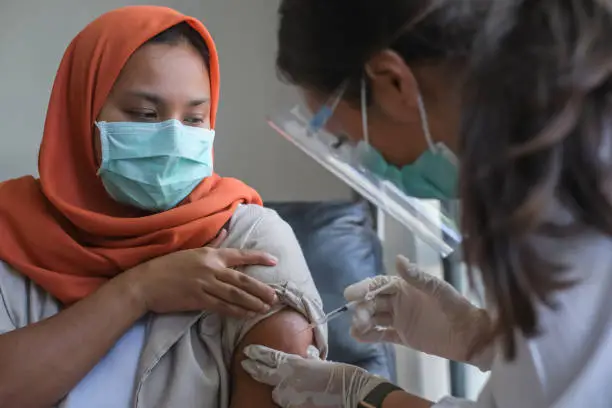
- Supporting Public Health Initiatives: Government agencies use medical grants to bolster public health initiatives aimed at preventing and controlling diseases. These initiatives include vaccination programs, disease surveillance, and health education campaigns.
- Addressing Health Disparities: Many medical grants are specifically tailored to underserved and vulnerable populations, ensuring that healthcare inequalities are addressed. These grants target minority communities, low-income individuals, and those residing in remote areas, striving to provide equitable access to healthcare resources.
Types of Medical Grants
Medical grants come in various forms, each serving distinct purposes:
- Government Grants: Federal, state, and local government bodies allocate substantial funding for healthcare-related initiatives. This includes research grants, public health programs, and grants to support Medicaid and other healthcare assistance programs.
- Private Foundation Grants: Numerous private foundations, endowed with significant resources, focus on healthcare grant programs. These foundations may specialize in areas such as global health, disease research, or healthcare access, offering financial support to organizations and individuals aligned with their mission.
- Disease-Specific Grants: Organizations dedicated to specific medical conditions, like cancer or diabetes, provide grants to fund research, patient support, and awareness campaigns. These grants are instrumental in driving progress in understanding and managing particular diseases.
- Community-Based Grants: Local nonprofits and community organizations play a vital role in addressing unique healthcare challenges within their regions. These grants often focus on preventive care, health education, and support services tailored to local needs.
Understanding the diverse sources of medical grants is crucial, as it allows individuals and organizations to identify potential funding opportunities that align with their healthcare objectives.
In essence, medical grants are not merely financial awards but symbols of hope and empowerment in the realm of healthcare. They provide the necessary resources to overcome financial obstacles, advance medical knowledge, enhance public health, and address healthcare disparities. As we delve deeper into the world of medical grants, subsequent sections will explore eligibility criteria, the application process, and essential tips for securing these invaluable resources to support healthcare endeavors.
Who Provides Medical Grants?
When it comes to securing essential funding for healthcare-related needs, understanding who provides medical grants is paramount. Medical grants, which serve as crucial financial lifelines in the realm of healthcare, are made available by various entities, each with its own mission and focus. These grants empower individuals and organizations to access the resources necessary to navigate the complex and often costly landscape of healthcare expenses.
Government Agencies:
One of the primary sources of medical grants is government agencies at various levels, including:
- Federal Government: Federal agencies such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) are instrumental in funding healthcare initiatives. They offer grants for medical research, public health programs, and healthcare access.
- State-Level Grants: State governments allocate funds for healthcare-related grants to address regional healthcare needs. These grants may support initiatives ranging from community health clinics to disease prevention programs.
- Local Healthcare Initiatives: Local municipalities and county governments also play a role in providing medical grants. These grants often focus on improving healthcare access and services within specific communities.
Private Foundations:
Numerous private foundations dedicate significant resources to healthcare-related grant programs. These foundations typically have specific areas of focus, including:
- Major Health Foundations: Prominent foundations like the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, and the Rockefeller Foundation are known for their substantial contributions to healthcare. They fund initiatives related to global health, healthcare access, and disease eradication.
- Disease-Specific Foundations: Many foundations concentrate on funding research and providing financial support to individuals affected by particular medical conditions. Examples include the American Cancer Society, the Alzheimer’s Association, and the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation.
- Community-Based Foundations: Local and regional foundations often offer grants to address healthcare disparities within their communities. These grants support healthcare education, preventive care, and support services for underserved populations.
Nonprofit Organizations:
Nonprofit organizations dedicated to healthcare advocacy and support also provide medical grants. These organizations, such as the Susan G. Komen Foundation and the American Heart Association, aim to improve healthcare outcomes and provide financial assistance to individuals facing medical challenges.
Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Companies:
In some cases, pharmaceutical and healthcare companies offer grants to support medical research and initiatives aligned with their corporate social responsibility goals. These grants may fund clinical trials, patient support programs, or healthcare access initiatives.
Universities and Research Institutions:
Academic institutions and research organizations often receive grants to conduct medical research. These grants contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge, leading to breakthroughs in treatments and therapies.
Community Organizations:
Local nonprofits and community organizations play a vital role in addressing healthcare needs at the grassroots level. They offer grants and financial assistance programs tailored to the specific healthcare challenges faced by their communities.
Importance of Medical Grants
In the intricate landscape of healthcare, the importance of medical grants cannot be overstated. These grants serve as lifelines, providing essential financial support to individuals, organizations, and researchers in their pursuit of accessible and high-quality healthcare. From reducing financial barriers to advancing medical knowledge and addressing healthcare disparities, medical grants play a pivotal role in shaping the present and future of healthcare.
- Reducing Financial Barriers
One of the foremost reasons for the importance of medical grants is their role in reducing financial barriers to healthcare access. Medical expenses can quickly spiral out of control, leaving individuals and families grappling with the daunting choice between their health and financial stability. Medical grants bridge this gap, covering costs such as hospital stays, surgeries, medications, and specialized treatments.
For those without adequate health insurance coverage or facing high deductibles and copayments, medical grants provide a glimmer of hope. They ensure that essential medical care is within reach, regardless of an individual’s financial circumstances. In doing so, medical grants contribute to improved health outcomes and a higher quality of life for countless individuals.
- Advancing Medical Research
The significance of medical grants extends beyond individual healthcare needs. These grants are instrumental in advancing medical research, a cornerstone of healthcare progress. Researchers and scientists rely on grants to fund critical studies, clinical trials, and investigations into new treatments and therapies.
Medical research grants enable scientists to explore the mechanisms of diseases, develop innovative medical technologies, and discover breakthroughs in patient care. Without such financial support, many groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in medical science would remain unattainable. In essence, medical grants are catalysts for progress, paving the way for improved healthcare treatments and outcomes.
- Supporting Public Health Initiatives
Government agencies use medical grants to bolster public health initiatives aimed at preventing and controlling diseases. These initiatives have a far-reaching impact, from vaccination campaigns that protect entire communities to disease surveillance programs that track and manage outbreaks.
Public health grants also fund health education initiatives, empowering individuals and communities with the knowledge and tools to make informed health decisions. By investing in these initiatives, medical grants contribute to disease prevention, healthier lifestyles, and overall community well-being.
- Addressing Healthcare Disparities
One of the most compelling aspects of the importance of medical grants is their role in addressing healthcare disparities. Many medical grants are specifically tailored to underserved and vulnerable populations, ensuring that healthcare inequalities are confronted head-on. These grants target minority communities, low-income individuals, and those residing in remote areas, striving to provide equitable access to healthcare resources.
By focusing on the unique needs of these populations, medical grants contribute to reducing health disparities and improving health equity. They work to level the playing field, ensuring that everyone, regardless of their background or circumstances, has access to the same standard of care.
Types of Medical Grants
When seeking financial assistance for healthcare-related needs, it’s essential to understand the various types of medical grants available. Medical grants are diverse and can cater to a wide range of healthcare initiatives, from supporting patient treatment to advancing medical research. Exploring these different grant categories is crucial for individuals and organizations looking to secure funding in the healthcare sector.
- Government Grants:
Government agencies at the federal, state, and local levels allocate substantial funds for healthcare-related grants. These grants serve various purposes:
- Federal Healthcare Grants: Federal agencies like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offer grants for medical research, public health programs, and initiatives targeting specific health issues.
- State-Level Grants: State governments provide grants to address regional healthcare needs. These grants may support healthcare access programs, community clinics, and public health campaigns.
- Local Healthcare Initiatives: Municipalities and county governments may offer grants for healthcare projects within their jurisdictions. These initiatives often focus on improving healthcare access and services at the local level.
2. Private Foundation Grants:
Private foundations endowed with substantial resources play a pivotal role in healthcare funding. These foundations often have specific areas of focus:
- Major Health Foundations: Prominent foundations like the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, and the Rockefeller Foundation dedicate resources to global health, healthcare access, and disease prevention. They fund initiatives with broad societal impact.
- Disease-Specific Foundations: Many foundations concentrate on particular medical conditions. For example, the American Cancer Society focuses on cancer-related grants, while the American Heart Association emphasizes cardiovascular health. These foundations support research, patient advocacy, and public education.
- Community-Based Foundations: Local and regional foundations address healthcare disparities within their communities. They provide grants for preventive care, health education, and support services tailored to local needs.
3. Nonprofit Organizations:
Nonprofit organizations that advocate for healthcare issues and support individuals also offer medical grants. These organizations, such as the Susan G. Komen Foundation and the March of Dimes, fund research, patient assistance programs, and awareness campaigns.
Disease-Specific Grants:
Medical grants often target specific diseases or health conditions. These grants support:
- Research: Funding research into the causes, treatments, and cures for particular diseases. Organizations like the Alzheimer’s Association and the Michael J. Fox Foundation focus on funding research related to their respective conditions.
- Patient Support: Providing financial assistance to individuals and families affected by specific diseases. These grants help cover medical expenses, support services, and therapies.
4. Community Grants:
Local nonprofit organizations and community groups frequently provide grants to address unique healthcare challenges within their regions. These grants often target preventive care, health education, and support services for underserved populations.
5. Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Company Grants:
Pharmaceutical companies and healthcare organizations occasionally offer grants to support medical research and initiatives that align with their corporate social responsibility goals. These grants may fund clinical trials, patient support programs, or healthcare access initiatives.
6. Research Institution Grants:
Academic institutions and research organizations receive grants to conduct medical research. These grants contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge, leading to breakthroughs in treatments and therapies.
Government Grants
Government grants are a critical source of funding for various healthcare-related initiatives at the federal, state, and local levels. These grants provide financial support to individuals, organizations, and institutions working to improve healthcare access, advance medical research, and address critical public health issues. Understanding government grants is essential for those seeking financial assistance in the healthcare sector.
Federal Healthcare Grants:
At the federal level, government agencies allocate significant funds for healthcare-related grants. These grants encompass a wide range of initiatives:
- National Institutes of Health (NIH): The NIH is a leading provider of medical research grants. It funds studies related to diseases, medical treatments, and public health. Researchers across the nation rely on NIH grants to conduct groundbreaking research.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC focuses on public health grants, supporting initiatives that prevent and control diseases, promote healthy behaviors, and enhance healthcare infrastructure.
- Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA): HRSA administers grants to improve healthcare access for underserved populations, enhance rural healthcare, and support healthcare workforce development.
- Medicaid and Medicare Grants: Federal programs like Medicaid and Medicare provide grants to states to support healthcare services for low-income individuals and seniors. These grants fund essential healthcare initiatives and ensure that vulnerable populations receive the care they need.
State-Level Grants:
State governments play a vital role in addressing regional healthcare needs. They allocate funds for a variety of healthcare-related programs and grants:
- Healthcare Access Initiatives: States often provide grants to bolster healthcare access in underserved areas. This may include supporting community clinics, expanding telehealth services, and increasing healthcare workforce capacity.
- Public Health Programs: Grants from state health departments fund public health programs that address issues such as immunization, disease surveillance, and health education.
- Health Insurance Assistance: Some states offer grants to nonprofit organizations that help individuals navigate health insurance options, apply for coverage, and understand their healthcare rights.
Local Healthcare Initiatives:
Municipalities and county governments also contribute to healthcare funding through local initiatives and grants:
- Community Health Centers: Local governments may support community health centers that provide primary care, dental services, and mental health support to residents in their jurisdictions.
- Preventive Healthcare: Grants from local governments often target preventive healthcare programs, including vaccinations, screenings, and wellness initiatives.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: Some local grants focus on improving healthcare infrastructure, such as upgrading healthcare facilities or expanding emergency medical services.
Application Process for Government Grants:
Applying for government grants can be a complex process. Each government agency or department may have its own application guidelines and requirements. Typically, the process involves:
- Identifying Eligibility: Determine whether your project or organization is eligible for the specific grant program. Eligibility criteria can vary widely.
- Researching Grant Opportunities: Research available government grants that align with your healthcare initiative. Government agencies often publish grant announcements and guidelines on their websites.
- Preparing a Strong Proposal: Craft a compelling grant proposal that outlines your project’s goals, objectives, budget, and expected outcomes. Be sure to adhere to the application guidelines provided by the granting agency.
- Submission and Review: Submit your grant application according to the agency’s instructions. Government grants undergo a rigorous review process, which may include peer review and evaluation by agency experts.
- Award and Reporting: If your grant is awarded, you will be required to fulfill reporting and accountability requirements outlined by the granting agency. This may include regular progress reports and financial documentation.
Federal Healthcare Grants
Federal healthcare grants represent a cornerstone of healthcare funding in the United States. These grants, provided by federal government agencies, serve a crucial role in supporting a wide array of healthcare-related initiatives, ranging from medical research and public health programs to healthcare access and services. Understanding the landscape of Federal Healthcare Grants is essential for those seeking financial assistance in the healthcare sector.
National Institutes of Health (NIH) Grants:
The National Institutes of Health, often referred to as NIH, is a premier provider of federal healthcare grants. It is composed of multiple institutes and centers, each specializing in different areas of medical research. NIH grants support research projects and studies aimed at advancing medical knowledge, developing treatments, and improving healthcare outcomes. Researchers across the nation rely on NIH grants to conduct groundbreaking research in fields such as cancer, cardiovascular health, infectious diseases, and more.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Grants:
The CDC, a federal agency focused on public health, plays a pivotal role in addressing healthcare challenges through its grants. CDC grants predominantly target public health initiatives designed to prevent and control diseases, promote healthy behaviors, and enhance healthcare infrastructure. These grants support programs related to disease surveillance, health education, immunizations, and emergency preparedness, among other critical public health efforts.
Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) Grants:
The HRSA is responsible for administering a range of federal healthcare grants that focus on healthcare access, workforce development, and support for underserved populations. HRSA grants support initiatives such as community health centers, rural healthcare access, telehealth services, and programs that bolster the healthcare workforce. These grants aim to improve healthcare delivery to vulnerable and underserved communities, ensuring that everyone has access to quality care.
Medicaid and Medicare Grants:
Federal programs like Medicaid and Medicare provide essential healthcare grants to states. These grants support healthcare services for low-income individuals and seniors. Medicaid grants, for example, fund healthcare for eligible low-income populations, while Medicare grants ensure that seniors have access to necessary medical care. These grants help alleviate the financial burden of healthcare expenses for some of the most vulnerable members of society.
The Application Process for Federal Healthcare Grants:
Applying for federal healthcare grants can be a rigorous process, and each federal agency may have its own specific guidelines and requirements. The application process typically includes the following steps:
- Eligibility Assessment: Determine whether your organization or project is eligible for the specific federal grant program. Eligibility criteria can vary significantly depending on the grant’s focus.
- Grant Research: Conduct thorough research to identify federal healthcare grant opportunities that align with your healthcare initiative. Federal agencies typically provide grant announcements and detailed guidelines on their websites.
- Proposal Development: Craft a compelling grant proposal that outlines your project’s objectives, goals, budget, and expected outcomes. Ensure that your proposal adheres to the application guidelines provided by the federal agency.
- Submission and Review: Submit your grant application according to the agency’s instructions and deadlines. Federal healthcare grants undergo a meticulous review process, often involving peer review and evaluation by agency experts.
- Award and Reporting: If your grant is awarded, you will be required to meet reporting and accountability requirements outlined by the federal agency. This may involve providing regular progress reports, financial documentation, and compliance with federal regulations.
State-Level Grants
State-level grants represent a significant source of funding for a wide range of healthcare initiatives within the United States. These grants are administered by state governments and are designed to address specific healthcare needs and challenges unique to each state. Understanding state-level grants is essential for individuals, organizations, and institutions seeking financial support for healthcare-related projects and programs.
Types of State-Level Grants:
State-level grants encompass various categories, each tailored to address specific healthcare concerns:
- Healthcare Access Grants: Many states offer grants to improve healthcare access, particularly in underserved and rural areas. These grants support initiatives such as the expansion of community health clinics, the establishment of telehealth services, and efforts to increase the capacity of healthcare providers.
- Public Health Programs: State health departments often provide grants to support public health programs. These programs may focus on disease prevention, health education, vaccination campaigns, and efforts to combat specific health challenges within the state.
- Mental Health and Substance Abuse Grants: Given the growing concern over mental health and substance abuse issues, states allocate grants to address these critical areas. These grants support mental health services, addiction treatment programs, and initiatives aimed at reducing the stigma surrounding mental health.
- Maternal and Child Health Grants: States prioritize the health of mothers and children by offering grants that support maternal and child health programs. These programs focus on prenatal care, child immunizations, maternal health education, and services for at-risk populations.
- Healthcare Workforce Development: States recognize the importance of a well-trained healthcare workforce and provide grants to institutions and programs that promote healthcare workforce development. These grants support initiatives like training healthcare professionals, expanding healthcare education, and increasing the number of healthcare providers.
The Application Process for State-Level Grants:
Applying for state-level grants typically involves several steps:
- Eligibility Check: Determine whether your project or organization is eligible for the specific state-level grant program. Eligibility criteria can vary widely based on the grant’s focus and the state’s priorities.
- Research Grant Opportunities: Research available state-level healthcare grants that align with your project’s goals. State health departments and government websites often provide information on available grants, including application guidelines.
- Proposal Development: Craft a compelling grant proposal that outlines your project’s objectives, budget, and expected outcomes. Ensure that your proposal aligns with the application guidelines provided by the state agency.
- Submission and Review: Submit your grant application according to the state’s instructions and deadlines. State-level grants undergo a review process, which may include evaluation by state experts and panels.
- Award and Reporting: If your grant is awarded, you will be required to fulfill reporting and accountability requirements outlined by the state agency. This may involve regular progress reports, financial documentation, and compliance with state regulations.
The Impact of State-Level Grants:
State-level grants have a significant impact on healthcare within each state. They:
- Improve Healthcare Access: Grants that support healthcare access initiatives increase the availability of medical services, particularly in underserved areas, enhancing healthcare access for residents.
- Enhance Public Health: Grants for public health programs help address and mitigate public health challenges, contributing to better health outcomes for communities.
- Support Vulnerable Populations: Many state-level grants are designed to support vulnerable populations, including low-income individuals, minorities, and those in rural areas, ensuring that they receive the care and services they need.
- Foster Workforce Development: Grants promoting healthcare workforce development help train and retain healthcare professionals, ensuring a skilled and diverse healthcare workforce.
Local Healthcare Initiatives
Local healthcare initiatives are a crucial component of the healthcare landscape, focusing on addressing unique healthcare challenges and needs within specific communities or regions. These initiatives, often supported by local governments, nonprofit organizations, and community groups, play a vital role in improving healthcare access, enhancing services, and promoting the well-being of residents. Understanding local healthcare initiatives is essential for individuals and organizations seeking to make a positive impact on community health.
Types of Local Healthcare Initiatives:
Local healthcare initiatives encompass a wide range of programs and projects, each tailored to address specific healthcare concerns within a community. Here are some common types:
- Community Health Clinics: Many communities establish community health clinics that provide primary care services, preventive care, and health education to residents. These clinics are often designed to serve low-income individuals and those without access to traditional healthcare providers.
- Telehealth Services: In remote or underserved areas, telehealth initiatives are becoming increasingly important. These programs offer remote medical consultations and services through digital platforms, expanding healthcare access for residents who may have limited transportation options.
- Health Education and Prevention Programs: Local healthcare initiatives frequently focus on health education and preventive measures. They may include initiatives to promote healthy lifestyles, encourage vaccination, and provide information on managing chronic conditions.
- Mental Health and Substance Abuse Services: Given the growing concerns surrounding mental health and substance abuse, many communities establish local initiatives to provide mental health services, counseling, and addiction treatment programs.
- Maternal and Child Health Services: Initiatives targeting maternal and child health aim to improve prenatal care, child immunization rates, and access to maternal and pediatric healthcare services.
Partnerships and Funding:
Local healthcare initiatives often rely on partnerships and funding from various sources:
- Local Governments: Municipalities and county governments allocate funds and resources to support local healthcare programs. These initiatives are typically aligned with the specific healthcare needs of the community.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Many nonprofit organizations, including healthcare foundations and community health nonprofits, collaborate with local communities to provide funding and expertise for healthcare initiatives.
- Healthcare Providers: Local hospitals, clinics, and healthcare providers often play an active role in supporting community health programs. They may offer resources, staff, and services to help address local healthcare challenges.
- Community Engagement: The active involvement of community members and volunteers is essential for the success of local healthcare initiatives. Volunteers often contribute their time and expertise to promote health and wellness within their communities.
The Impact of Local Healthcare Initiatives:
Local healthcare initiatives have a profound impact on community health:
- Improved Access: Initiatives such as community health clinics and telehealth services increase access to healthcare for residents who may otherwise face barriers to care.
- Better Health Outcomes: Health education and prevention programs contribute to healthier lifestyles and reduced rates of preventable diseases within communities.
- Support for Vulnerable Populations: Local initiatives often focus on serving vulnerable populations, including low-income individuals, minorities, and the elderly, ensuring that they receive appropriate healthcare services.
- Mental Health and Addiction Support: Initiatives addressing mental health and substance abuse provide critical services to individuals struggling with these issues, promoting overall well-being.
- Maternal and Child Health: Programs targeting maternal and child health help improve the health and safety of expectant mothers and children, leading to healthier families and communities.
Getting Involved in Local Healthcare Initiatives:
Individuals and organizations interested in supporting local healthcare initiatives can take several steps:
- Research Local Needs: Understand the specific healthcare needs and challenges within your community to identify areas where your involvement can make a difference.
- Volunteer: Consider volunteering your time, skills, or resources to support local healthcare programs and initiatives.
- Collaborate: Partner with local healthcare providers, nonprofits, and community groups to collectively address healthcare challenges and create meaningful solutions.
- Advocate: Advocate for increased funding and resources for local healthcare initiatives to ensure their sustainability and effectiveness.
Private foundation grants represent a significant source of funding for a wide range of charitable initiatives, including those in the healthcare sector. These grants are offered by private foundations established by individuals, families, or corporations with a philanthropic mission. Private foundation grants play a vital role in supporting medical research, healthcare access, and various healthcare-related projects that aim to improve public health and well-being.
Types of Private Foundations:
Private foundations are diverse, and they often focus on specific areas of interest. In the realm of healthcare, there are several types of private foundations:
- Major Health Foundations: Prominent foundations, such as the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, and the Rockefeller Foundation, are known for their substantial contributions to healthcare initiatives. They support a wide array of programs, including global health, healthcare access, and disease prevention.
- Disease-Specific Foundations: Many private foundations concentrate on funding research and providing financial support to individuals affected by particular medical conditions. Examples include the American Cancer Society, the Alzheimer’s Association, and the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation.
- Community-Based Foundations: Local and regional foundations focus on addressing healthcare disparities within their communities. These foundations support healthcare education, preventive care, and support services tailored to local needs.
Focus Areas of Private Foundation Grants:
Private foundation grants can encompass various healthcare focus areas, including:
- Medical Research: Foundations often fund medical research projects aimed at understanding diseases, developing new treatments, and advancing medical science.
- Healthcare Access: Some foundations prioritize improving healthcare access, particularly for underserved populations. This may include funding community clinics, health education programs, and initiatives that expand healthcare services.
- Disease Prevention: Grants support initiatives that focus on disease prevention, including vaccination campaigns, public health education, and lifestyle interventions.
- Patient Support: Foundations may provide grants to support patients and their families, covering medical expenses, transportation, and essential support services.
Applying for Private Foundation Grants:
Securing a private foundation grant typically involves the following steps:
- Research Grant Opportunities: Identify private foundations that align with your healthcare initiative. Explore their websites, review their grant guidelines, and understand their funding priorities.
- Contact the Foundation: Reach out to the foundation’s staff or program officers to discuss your project and seek guidance on the application process.
- Craft a Compelling Proposal: Develop a well-structured grant proposal that clearly outlines your project’s objectives, goals, budget, and expected outcomes. Ensure that your proposal aligns with the foundation’s mission and focus areas.
- Submission and Review: Submit your grant application by the foundation’s deadline. Private foundation grants typically go through a rigorous review process, which may involve peer review and expert evaluation.
- Award and Reporting: If your grant is awarded, you will be required to fulfill reporting and accountability requirements outlined by the foundation. This may include regular progress reports and financial documentation.
The Impact of Private Foundation Grants:
Private foundation grants have a significant impact on healthcare:
- Advancing Medical Knowledge: Funding for medical research leads to breakthroughs in understanding diseases and developing new treatments, ultimately improving patient care.
- Enhancing Healthcare Access: Grants that support healthcare access initiatives ensure that individuals, particularly underserved populations, can access essential healthcare services.
- Addressing Healthcare Disparities: Foundations that target local communities and vulnerable populations help address healthcare inequalities and improve health outcomes.
- Supporting Patients: Grants that provide patient support alleviate the financial burden of medical expenses, enhancing the quality of life for those facing health challenges.
Major Health Foundations
Major health foundations represent a powerful force in the realm of healthcare philanthropy. These foundations, often endowed with substantial resources, play a pivotal role in addressing global health challenges, expanding healthcare access, and advancing medical research. They are committed to improving public health and well-being on a global scale. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the world of major health foundations, their missions, and their significant impact on healthcare worldwide.
Prominent Major Health Foundations:
Several major health foundations are recognized for their significant contributions to healthcare and their dedication to addressing pressing health issues. These include:
- Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation: One of the largest and most influential philanthropic organizations in the world, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation focuses on global health, poverty alleviation, and education. Its healthcare initiatives span areas such as infectious diseases, maternal and child health, nutrition, and healthcare delivery systems.
- Robert Wood Johnson Foundation: With a mission to improve health and healthcare in the United States, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation is dedicated to advancing policies, practices, and systems that promote equitable access to high-quality healthcare.
- Rockefeller Foundation: The Rockefeller Foundation has a storied history of supporting healthcare initiatives. It addresses issues such as pandemic preparedness, health data, and access to healthcare for vulnerable populations.
Areas of Focus:
Major health foundations concentrate their efforts on various areas within the healthcare sector:
- Global Health: These foundations are at the forefront of global health initiatives, tackling infectious diseases like HIV/AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis, as well as addressing broader issues such as vaccine distribution and healthcare infrastructure in low-income countries.
- Healthcare Access: Major health foundations work to expand access to healthcare services, particularly for underserved populations. This may involve supporting community clinics, telemedicine, and healthcare workforce development.
- Disease Prevention: Foundations fund initiatives that prioritize disease prevention, including vaccination campaigns, health education, and lifestyle interventions aimed at reducing the burden of chronic diseases.
- Health Equity: Many foundations are committed to addressing health disparities and promoting health equity. They focus on reducing inequalities in healthcare access and outcomes among different population groups.
Impact on Healthcare:
The impact of major health foundations on healthcare is profound:
- Medical Research: These foundations fund cutting-edge medical research, leading to breakthroughs in treatment and prevention. Their investments have been instrumental in advancing our understanding of diseases and improving patient care.
- Vaccine Development: Foundations have played a pivotal role in accelerating vaccine development and distribution, particularly during global health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Health Systems Strengthening: Major health foundations contribute to building robust healthcare systems, ensuring that communities have access to quality care and resources during times of need.
- Health Policy Advocacy: They advocate for policies that improve healthcare access and outcomes, promoting equitable health solutions.
Collaborations and Partnerships:
Major health foundations often collaborate with governments, non-governmental organizations, healthcare providers, and research institutions to amplify their impact. These partnerships enhance the reach and effectiveness of healthcare initiatives, fostering innovation and driving progress in the field.
Future Outlook:
The role of major health foundations is poised to grow even more significant in the future. As the world faces evolving health challenges, including pandemics, chronic diseases, and healthcare inequalities, these foundations will continue to be at the forefront of global health efforts.
Disease-Specific-Foundations
Disease-specific foundations are a vital force in the realm of healthcare philanthropy. These foundations are dedicated to addressing the unique challenges posed by specific medical conditions, advocating for patients, funding research, and providing support to individuals and families affected by these diseases. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the world of disease-specific foundations, their missions, and their significant impact on healthcare and patient communities.
Understanding Disease-Specific Foundations:
Disease-specific foundations are nonprofit organizations that focus their efforts on a particular medical condition or group of related conditions. They are driven by a commitment to improving the lives of individuals affected by these diseases, whether through research, education, patient support, or advocacy. Each foundation typically has a clear mission and mandate centered on a specific disease or medical condition.
Examples of Disease-Specific Foundations:
There are numerous disease-specific foundations addressing a wide range of medical conditions. Some prominent examples include:
- American Cancer Society: Dedicated to the fight against cancer, this foundation funds research, provides patient support, and raises awareness about cancer prevention and treatment.
- Alzheimer’s Association: Focused on Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, this foundation supports research into the causes and treatments of these conditions, while also offering resources and support to patients and caregivers.
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation: This foundation is dedicated to improving the lives of those with cystic fibrosis through research, care, and advocacy efforts aimed at finding a cure for the disease.
Areas of Focus:
Disease-specific foundations concentrate their efforts on various aspects related to their chosen medical conditions:
- Medical Research: These foundations fund research to better understand the causes, mechanisms, and potential treatments for the disease. Research efforts often lead to groundbreaking discoveries that advance medical knowledge and improve patient outcomes.
- Patient Support: Foundations offer resources and support services to individuals and families affected by the disease. This may include access to information, counseling, financial assistance, and patient advocacy.
- Awareness and Education: Disease-specific foundations work to raise awareness about the condition, promoting early detection, prevention, and education within communities and the healthcare sector.
- Advocacy: Many foundations advocate for public policies that benefit patients, such as increased funding for research, improved access to treatments, and better insurance coverage.
Impact on Healthcare:
The impact of disease-specific foundations on healthcare is profound:
- Advancing Medical Science: These foundations contribute to significant advancements in understanding the disease, leading to improved diagnostic tools, treatment options, and potential cures.
- Patient Empowerment: By offering support and resources to patients and their families, these foundations empower individuals to better manage their condition and make informed healthcare decisions.
- Funding Research: Disease-specific foundations are often major funders of medical research, leading to innovative therapies and breakthroughs in the field.
- Policy Influence: Through advocacy efforts, these foundations influence healthcare policy changes that benefit patients and improve healthcare systems.
Partnerships and Collaborations:
Disease-specific foundations frequently collaborate with healthcare institutions, research organizations, pharmaceutical companies, and government agencies to achieve their goals. These partnerships enhance their impact by facilitating the development of treatments, increasing research funding, and expanding patient support networks.
Future Outlook:
As our understanding of diseases and medical conditions continues to evolve, disease-specific foundations will play an increasingly pivotal role in healthcare. The knowledge, resources, and advocacy they provide are essential in the pursuit of better treatments, improved patient care, and, in some cases, the ultimate goal of finding cures for these conditions.
Community-Based Foundations
Community-based foundations are essential pillars of support within local and regional communities. These nonprofit organizations are dedicated to addressing specific healthcare challenges, improving health outcomes, and enhancing the overall well-being of the populations they serve. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the world of community-based foundations, their missions, and their significant impact on local healthcare initiatives.
Understanding Community-Based Foundations:
Community-based foundations are nonprofit organizations that operate at the local or regional level. They are often established and governed by community members who have a vested interest in addressing healthcare disparities and enhancing health outcomes within their specific geographic area. These foundations typically have a clear mission centered on the health and well-being of the communities they serve.
Roles and Responsibilities:
Community-based foundations play various roles in supporting healthcare and community health initiatives:
- Resource Allocation: These foundations raise funds and allocate resources to address local healthcare challenges. They may provide financial support to healthcare organizations, clinics, and community health programs.
- Capacity Building: Foundations work to strengthen the healthcare infrastructure within their communities. This includes supporting healthcare workforce development, expanding healthcare facilities, and improving access to care.
- Health Promotion: Many community-based foundations focus on health promotion and preventive measures. They may initiate public health campaigns, support vaccination drives, and promote healthy lifestyles.
- Advocacy: Foundations advocate for policies that improve healthcare access, reduce healthcare disparities, and promote community well-being.
Examples of Community-Based Foundations:
Community-based foundations are diverse and tailored to the unique healthcare needs of their communities. Some examples include:
- The California Endowment: This foundation focuses on improving the health of Californians, particularly underserved communities. It supports various health initiatives, including access to care, mental health services, and health equity.
- The Cleveland Foundation: Serving the Greater Cleveland area, this foundation supports numerous healthcare programs and initiatives that aim to improve the overall well-being of the community, including healthcare access and education.
- The Chicago Community Trust: Focused on the Chicagoland area, this foundation addresses healthcare disparities and promotes health equity through funding, advocacy, and community engagement.
Impact on Local Healthcare:
The impact of community-based foundations on local healthcare is significant:
- Enhanced Healthcare Access: Foundations often fund projects that increase access to healthcare services, particularly for underserved populations.
- Health Education and Promotion: They engage in health education efforts that empower community members with knowledge and encourage healthy behaviors.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: These foundations invest in healthcare infrastructure, improving the quality and availability of healthcare services within the community.
- Reduced Disparities: By targeting healthcare disparities, foundations help ensure that all community members have equitable access to healthcare and health resources.
Partnerships and Collaborations:
Community-based foundations actively collaborate with local healthcare providers, nonprofit organizations, public health agencies, and community leaders to maximize their impact. These partnerships enhance the reach and effectiveness of healthcare initiatives and facilitate the sharing of resources and expertise.
Future Outlook:
Community-based foundations are poised to play an increasingly crucial role in healthcare as they adapt to evolving community needs. They will continue to be at the forefront of addressing healthcare disparities, promoting health equity, and enhancing overall community health.
Eligibility and Application Process
Eligibility Criteria and Application Process for grants are crucial aspects that grant seekers must understand to secure funding successfully. Whether you’re seeking medical, educational, or research grants, a clear comprehension of these elements is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of eligibility criteria and the grant application process, shedding light on what you need to know to navigate this often intricate terrain effectively.
Eligibility Criteria:
Eligibility criteria are the specific requirements and conditions that grant applicants must meet to be considered for funding. These criteria vary significantly from one grant to another and are typically set by the grant-making organization or agency. Here are common factors considered in eligibility criteria:
- Type of Organization: Grants may be available to various types of organizations, such as nonprofit organizations, educational institutions, research institutions, healthcare providers, and more. Eligibility often depends on the applicant’s legal structure and mission.
- Geographic Location: Some grants are geographically restricted, targeting specific regions, states, or countries. Eligibility may be determined based on the location of the applicant and the intended beneficiaries.
- Project Focus: Grants are typically designed for specific purposes, such as medical research, education, community development, or environmental conservation. Eligibility may hinge on the alignment of the proposed project with the grant’s focus area.
- Project Stage: Some grants are intended for projects at specific stages of development. For example, seed grants may be aimed at early-stage research, while implementation grants support established programs.
- Financial Status: Eligibility criteria may consider the financial health and stability of the applicant organization. This can include factors such as annual revenue, budget size, and financial sustainability.
- Collaboration: Certain grants may require collaboration with other organizations, institutions, or stakeholders. Meeting these partnership requirements may be essential for eligibility.
Application Process:
The grant application process can be intricate and competitive. To navigate it successfully, follow these key steps:
- Research Grant Opportunities: Begin by identifying grant opportunities that align with your project or organization’s goals. Explore grant databases, foundation websites, and government agencies to find suitable opportunities.
- Review Eligibility Criteria: Carefully review the eligibility criteria for each grant you plan to apply for. Ensure that your organization and project meet these requirements before proceeding.
- Prepare a Grant Proposal: Craft a compelling grant proposal that outlines your project’s objectives, goals, budget, and expected outcomes. Address how your project aligns with the grant’s focus and mission. Be clear and concise in your writing.
- Gather Required Documents: Grants often require various supporting documents, such as financial statements, letters of recommendation, project budgets, and organizational information. Collect and organize these documents in advance.
- Complete the Application Form: Follow the grant-maker’s instructions for submitting your application. This often involves completing an online application form or submitting a physical application package. Be thorough and accurate in filling out all required fields.
- Submit the Application: Submit your grant application by the specified deadline. Late applications are typically not accepted, so adhere to the timeline provided by the grant-maker.
- Follow-Up and Communication: After submitting your application, you may receive requests for additional information or clarifications. Be prepared to respond promptly and professionally to any inquiries from the grant-making organization.
- Grant Review and Decision: Grant applications go through a review process, which may include peer review, expert evaluation, and consideration by a review panel. The grant-making organization will communicate its decision, whether approval or rejection, within a specified timeframe.
- Grant Management: If your grant is approved, you will need to adhere to the grant’s terms and conditions, reporting requirements, and deadlines for project implementation. Proper grant management is crucial to ensuring compliance and successful project execution.
Applying for Medical Grants: A Comprehensive Guide to Securing Healthcare Funding
Medical grants play a pivotal role in advancing healthcare, supporting critical research, and ensuring access to quality medical services. Whether you are a healthcare provider, researcher, nonprofit organization, or an individual facing medical challenges, understanding how to apply for medical grants is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the process of applying for medical grants, offering valuable insights and tips to increase your chances of success.
Why Pursue Medical Grants:
Medical grants offer significant advantages for both individuals and organizations committed to improving healthcare:
- Funding Medical Research: Grants support groundbreaking medical research, leading to new treatments, therapies, and cures for diseases and health conditions.
- Enhancing Healthcare Access: Grants can bolster healthcare access by funding clinics, equipment, and services for underserved populations.
- Supporting Nonprofit Organizations: Nonprofits can secure funding through grants to expand their healthcare initiatives, address community health needs, and provide crucial support to patients.
- Easing Financial Burden: For individuals facing medical expenses, certain grants can help alleviate the financial burden of treatments, medications, and medical equipment.
Key Steps in Applying for Medical Grants:
- Identify Suitable Grant Opportunities:
- Conduct thorough research to identify grants that align with your medical project, research focus, or healthcare needs.
- Utilize grant databases, foundation websites, and government agencies to find relevant opportunities.
- Ensure the grant’s mission and goals align with your project or medical condition.
- Review Grant Guidelines:
- Carefully read and understand the grant guidelines provided by the grant-making organization.
- Pay close attention to eligibility criteria, application deadlines, required documents, and reporting obligations.
- Prepare a Strong Proposal:
- Craft a compelling grant proposal that clearly outlines your project’s objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
- Highlight the significance of your project or research in addressing a specific medical need or advancing healthcare.
- Gather Supporting Documents:
- Assemble all required supporting documents, such as budget estimates, letters of support, and any necessary certifications.
- Ensure that your documentation is complete and well-organized to streamline the application process.
- Complete the Application Form:
- Follow the instructions provided by the grant-maker to complete the application form accurately.
- Be concise, yet comprehensive, in your responses, addressing all relevant questions and criteria.
- Submit the Application:
- Submit your grant application by the specified deadline. Late submissions are typically not considered.
- Verify that all required materials are included before submission.
- Follow-Up and Communication:
- Be prepared to respond to any requests for additional information or clarifications from the grant-making organization.
- Maintain clear and professional communication throughout the application process.
- Grant Review and Decision:
- Grant applications undergo a review process, which may include peer review, expert evaluation, and consideration by a review panel.
- The grant-making organization will communicate its decision, whether approval or rejection, within a specified timeframe.
- Grant Management:
- If your grant is approved, adhere to the grant’s terms and conditions, reporting requirements, and deadlines for project implementation.
- Proper grant management is essential to ensure compliance and successful project execution.
Tips for Success:
- Tailor your proposal to align with the grant’s objectives and mission.
- Highlight the potential impact and benefits of your medical project or research.
- Seek advice or mentorship from experienced grant seekers or professionals in your field.
- Review and proofread your application for accuracy and clarity.
- Be persistent and prepared to apply for multiple grants to increase your chances of securing funding.
Researching Grant Opportunities: A Comprehensive Guide to Finding Funding
Grants are a valuable source of funding for a wide range of projects, from scientific research and nonprofit initiatives to educational programs and community development. However, finding the right grant opportunities that align with your goals and mission can be a daunting task. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the process of researching grant opportunities, offering valuable insights and strategies to help you discover the funding you need.
Why Researching Grant Opportunities is Crucial:
Thoroughly researching grant opportunities is crucial for several reasons:
- Alignment with Goals: Identifying grants that align with your project or organization’s goals ensures that your efforts are well-supported and that your mission is in sync with the grantor’s objectives.
- Optimizing Resources: Conducting research helps you focus your time and resources on grants that have the highest likelihood of success, saving you from applying for unsuitable opportunities.
- Maximizing Impact: Finding the right grants allows you to secure funding that can have a significant impact on your project, research, or initiative, ultimately benefiting your target audience or community.
Steps to Effective Grant Research:
- Define Your Objectives:
- Begin by clearly defining your project’s objectives, goals, and the type of funding you require.
- Determine the specific purpose for which you need funding, whether it’s research, community development, education, or healthcare.
- Utilize Online Resources:
- Explore online grant databases and search engines dedicated to aggregating grant opportunities.
- Websites like Grants.gov, Foundation Directory Online, and Candid’s GuideStar provide extensive grant listings and search functionalities.
- Access Government Resources:
- Government agencies, both federal and state, offer various grant programs. Visit government websites to explore available opportunities.
- Consider specialized federal agencies like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) or the National Science Foundation (NSF) for research-focused grants.
- Engage with Foundations and Nonprofits:
- Foundation websites often feature information on their grant programs, eligibility criteria, and application processes.
- Many nonprofits and charitable organizations offer grants to support specific causes. Investigate these opportunities based on your mission.
- Network and Seek Recommendations:
- Leverage your professional network to seek recommendations on grants that may align with your goals.
- Attend grant-related conferences, workshops, and webinars to connect with experts and stay informed about new opportunities.
- Check Grantor Websites:
- Visit the websites of potential grantors to access detailed information about their funding priorities and application procedures.
- Review past grant recipients and project descriptions to gauge alignment with your work.
- Subscribe to Grant Alerts:
- Many grant-related websites and platforms offer email alerts or newsletters that notify subscribers of new grant opportunities.
- Subscribe to these services to receive timely updates on grants that match your interests.
- Read and Understand Guidelines:
- Thoroughly read the guidelines and eligibility criteria provided by grantors to determine if you meet the requirements.
- Pay attention to deadlines, submission instructions, and any specific documents or materials required.
- Organize and Prioritize:
- Create a systematic approach to organize grant opportunities based on deadlines, eligibility, and alignment with your objectives.
- Prioritize opportunities that best fit your needs and have a high potential for success.
- Prepare and Submit Applications:
- Once you’ve identified suitable grant opportunities, prepare compelling grant applications that clearly articulate your project’s significance and impact.
- Follow the application instructions precisely and submit your proposals by the specified deadlines.
Preparing a Strong Application: Key Strategies for Grant Success
A well-prepared grant application is the gateway to securing funding for your project or initiative. Whether you’re seeking support for research, community development, education, or healthcare, a strong application can significantly increase your chances of success. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore essential strategies to help you prepare a compelling and competitive grant application.
Why a Strong Application Matters:
A strong grant application is crucial for several reasons:
- Competitive Edge: Grant competitions are often fierce, and a well-prepared application can give you a competitive advantage.
- Clear Communication: A strong application effectively communicates your project’s goals, objectives, and potential impact to the grant reviewers.
- Maximizing Funding: A compelling application increases the likelihood of receiving the funding needed to execute your project successfully.
Key Strategies for Preparing a Strong Application:
- Understand the Grant Guidelines:
- Thoroughly review the grant guidelines provided by the grant-making organization. Pay attention to eligibility criteria, submission deadlines, and any specific requirements.
- Ensure that your project aligns with the grant’s mission and objectives.
- Craft a Clear and Concise Proposal:
- Your proposal should clearly state the problem you aim to address, your project’s goals, and the methods you’ll employ to achieve them.
- Be concise and avoid jargon. Make your proposal accessible to reviewers who may not be experts in your field.
- Demonstrate Significance and Impact:
- Clearly articulate the significance of your project and how it addresses a critical need or issue.
- Describe the potential impact of your project on the target audience, community, or field of study.
- Budget Wisely:
- Develop a detailed and realistic budget that aligns with your project’s goals and objectives.
- Ensure that your budget is well-organized, transparent, and justifiable.
- Provide Supporting Evidence:
- Back your proposal with strong evidence, including relevant research, data, and statistics.
- Include citations and references where appropriate to validate your claims.
- Engage Stakeholders:
- Demonstrate community or stakeholder support for your project through letters of endorsement or partnership agreements.
- Highlight any collaboration with other organizations or institutions.
- Adhere to Formatting and Submission Guidelines:
- Follow the grantor’s formatting and submission instructions meticulously.
- Ensure that your application is error-free, well-structured, and easy to navigate.
- Review and Proofread:
- Carefully proofread your application to eliminate grammatical errors and typos.
- Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure clarity and coherence.
- Address Evaluation and Reporting Requirements:
- Understand the grant’s evaluation criteria and reporting obligations.
- Outline how you plan to measure the success of your project and track outcomes.
- Meet Submission Deadlines:
- Submit your application well in advance of the deadline to avoid last-minute technical issues.
- Late submissions are typically not accepted.
- Follow-Up and Stay Informed:
- After submitting your application, be prepared to respond to any requests for additional information or clarifications from the grant-making organization.
- Stay informed about the grant review process and anticipate when decisions are expected to be communicated.
- Seek Professional Advice:
- If you are new to grant applications or require specialized knowledge, consider seeking advice or consulting with experts in your field or grant writing professionals.
Submission and Follow-Up: Navigating the Final Stages of Grant Applications
The process of securing grant funding doesn’t end when you hit the “submit” button on your application. In fact, what you do after submission and during the follow-up phase can significantly impact the outcome of your grant request. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the critical steps involved in the submission and follow-up phases of grant applications, offering valuable insights and strategies to help you maximize your chances of success.
The Importance of Submission and Follow-Up:
Submission and follow-up are essential components of the grant application process for several reasons:
- Ensure Compliance: Proper submission ensures that your application meets all requirements, increasing the likelihood of being considered by the grant review committee.
- Clarify and Enhance: During the follow-up phase, you have the opportunity to address any questions or concerns from reviewers, clarifying your proposal and potentially enhancing your application.
- Demonstrate Engagement: Active follow-up demonstrates your commitment and enthusiasm for the grant, which can leave a positive impression on grantors.
Submission Phase:
- Review Your Application: Before submitting, thoroughly review your application for completeness, accuracy, and adherence to guidelines.
- Verify Attachments: Ensure all required attachments, such as letters of support or budgets, are included and correctly formatted.
- Submit Early: Submit your application well in advance of the deadline to avoid technical issues or last-minute complications.
- Confirmation: After submission, confirm that your application was received by the grant-making organization. Retain a copy of the submission confirmation.
- Stay Informed: Monitor communication from the grantor for any requests for additional information or clarifications.
Follow-Up Phase:
- Acknowledgment of Receipt: If you don’t receive an acknowledgment of receipt shortly after submission, consider following up with the grantor to confirm they received your application.
- Response to Queries: Be prepared to respond promptly to any questions or queries from the grant review committee. Provide clear and concise answers, addressing their concerns.
- Additional Information: If requested, submit any additional information or documentation as requested by the grantor.
- Demonstrate Commitment: Use follow-up interactions to reiterate your commitment to the project and your appreciation for the opportunity.
- Stay Patient and Professional: Remain patient and professional throughout the follow-up phase, even if there are delays or challenges in communication.
- Meeting Requests: If appropriate, be open to requests for meetings or interviews with the grant review committee. These interactions can provide further insights into your proposal.
Tips for Effective Follow-Up:
- Organization: Maintain a well-organized record of all interactions, correspondence, and documents related to your grant application.
- Be Responsive: Respond to grantor inquiries or requests as quickly as possible, demonstrating your dedication to the process.
- Clarity: Ensure that your responses are clear, concise, and directly address any questions or concerns raised by reviewers.
- Professionalism: Maintain a professional and respectful tone in all interactions, whether written or verbal.
- Seek Guidance: If you’re uncertain about how to respond to a specific request or query, consider seeking guidance from mentors, peers, or grant writing professionals.
- Persistence: Don’t hesitate to follow up if you haven’t received a response within a reasonable timeframe. Sometimes, grantors may require gentle reminders.
Tips for a Successful Medical Grant Application: Unlocking Funding for Healthcare Initiatives
Medical grants are a critical source of funding for healthcare professionals, researchers, organizations, and individuals seeking to advance healthcare, conduct medical research, or address pressing health issues. However, securing medical grant funding can be highly competitive and challenging. To increase your chances of success, it’s essential to prepare a compelling and well-structured grant application. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore valuable tips to help you navigate the complex process of applying for medical grants effectively.
1. Begin with a Clear and Compelling Project Idea:
- Before you start drafting your grant application, ensure that your project idea is well-defined, relevant, and addresses a specific healthcare need or research question.
- Clearly articulate the significance of your project and its potential impact on healthcare or patient outcomes.
2. Carefully Review Grant Guidelines:
- Thoroughly read and understand the grant guidelines provided by the grant-making organization. Pay close attention to eligibility criteria, submission deadlines, and any specific requirements or preferences.
- Ensure that your project aligns with the grant’s mission and objectives.
3. Tailor Your Proposal to the Grant’s Objectives:
- Customize your grant proposal to align seamlessly with the goals and priorities of the grantor. Highlight how your project directly addresses the grant’s focus areas.
- Use language and terminology consistent with the grant’s mission to demonstrate alignment.
4. Demonstrate a Strong Understanding of the Problem:
- Clearly define the healthcare problem or research question you aim to address in your grant proposal.
- Provide data, evidence, and relevant statistics to underscore the urgency and significance of the issue.
5. Develop a Detailed and Realistic Budget:
- Create a comprehensive budget that accurately reflects the financial requirements of your project. Ensure that it is well-organized, transparent, and justifiable.
- Clearly outline how grant funds will be allocated to different project components, such as personnel, equipment, research materials, and other expenses.
6. Gather Strong Supporting Evidence:
- Back your proposal with robust supporting evidence, including peer-reviewed studies, clinical data, or similar research findings.
- Cite relevant literature and research to demonstrate the feasibility and potential success of your project.
7. Engage Stakeholders and Partners:
- If applicable, demonstrate collaboration and support from relevant stakeholders, institutions, or organizations. Letters of support or partnership agreements can strengthen your proposal.
- Highlight any existing collaborations that contribute to the project’s credibility.
8. Craft a Clear and Convincing Narrative:
- Write a well-structured and engaging narrative that clearly communicates your project’s goals, methods, and expected outcomes.
- Avoid jargon and complex language that may hinder reviewers’ understanding of your proposal.
9. Seek Feedback and Peer Review:
- Request feedback on your grant proposal from peers, mentors, or experts in your field. Constructive criticism can help identify areas for improvement.
- Revise and refine your proposal based on the feedback received.
10. Proofread and Edit Carefully:
– Ensure that your proposal is easy to read and follows the grantor’s formatting guidelines.
11. Submit Early and Prepare for Follow-Up:
– Be prepared for follow-up communication with the grantor, such as requests for additional information or clarifications.
12. Be Patient and Persistent:
– Maintain professionalism and a positive attitude throughout the process.
Clearly Define Your Medical Needs: A Crucial Step in Securing Healthcare Funding
When seeking medical grants or financial support for healthcare needs, it’s essential to start with a clear and precise definition of your medical needs. Whether you’re an individual seeking assistance with medical expenses or a healthcare organization aiming to fund critical initiatives, a well-defined understanding of your needs is the foundation for a successful grant application. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the importance of clearly defining your medical needs and provide insights into the process.
The Significance of Clearly Defined Medical Needs:
- Alignment with Grant Opportunities: Defining your medical needs ensures that you can identify grant opportunities that specifically address those needs. This alignment is essential for a successful application.
- Focused Proposal Development: A clear understanding of your needs allows you to develop a focused and tailored proposal that directly addresses the identified medical challenges or requirements.
- Impactful Communication: Clear articulation of your medical needs enables you to effectively communicate the urgency and importance of your request to grant reviewers or potential donors.
Steps to Clearly Define Your Medical Needs:
- Identify the Medical Issue:
- Begin by identifying the specific medical issue or challenge you are facing. Is it related to a diagnosis, treatment, medical equipment, research, or healthcare access?
- Gather Relevant Information:
- Collect all relevant medical information, including medical records, diagnostic reports, treatment plans, and cost estimates. These documents provide a factual basis for your needs.
- Consult with Healthcare Professionals:
- Seek advice and consultations from healthcare professionals, physicians, or specialists who can provide insights into your medical condition and its requirements.
- Quantify Financial Needs:
- Calculate the financial aspect of your medical needs, including anticipated expenses for treatments, medications, surgeries, medical equipment, or research-related costs.
- Consider Long-Term and Immediate Needs:
- Distinguish between long-term and immediate medical needs. Some needs may require ongoing support, while others may be one-time expenses.
- Assess the Impact on Your Life or Organization:
- Reflect on how the medical needs impact your life, well-being, or the goals and mission of your healthcare organization. Clearly express the significance of addressing these needs.
- Prioritize Your Needs:
- Prioritize your medical needs based on urgency, criticality, and the potential for positive outcomes. This will guide your approach to seeking funding.
Tips for Effective Definition of Medical Needs:
- Use Specific Language: Avoid vague descriptions and use specific medical terminology to accurately convey your needs.
- Provide Context: Offer context about your medical condition or the healthcare challenges you’re addressing. Explain the background and history, if relevant.
- Include Supporting Documentation: Attach relevant medical records, reports, and financial estimates to substantiate your needs.
- Quantify Costs: Whenever possible, provide precise financial figures to show the exact amount needed to address the medical issue.
- Highlight Impact: Emphasize the potential impact of addressing these needs on your health, quality of life, or the healthcare outcomes you aim to achieve.
- Align with Grant Criteria: Ensure that your defined needs align with the specific criteria and priorities of the grant you are applying for.
Showcasing Impact and Outcomes: Demonstrating the Value of Your Healthcare Initiatives
Effectively showcasing the impact and outcomes of your healthcare initiatives is a vital aspect of securing funding, engaging stakeholders, and driving positive change in the healthcare landscape. Whether you are a healthcare organization, a researcher, or an individual seeking support for your healthcare project, conveying the results and benefits of your efforts is key to gaining credibility and attracting support. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the significance of showcasing impact and outcomes and provide strategies to help you effectively demonstrate the value of your healthcare initiatives.
The Importance of Showcasing Impact and Outcomes:
- Transparency and Accountability: Demonstrating the impact and outcomes of your healthcare initiatives fosters transparency and accountability. It allows stakeholders, including funders and the public, to assess how resources are being used.
- Attracting Funding: Grant-making organizations, donors, and investors are more likely to support initiatives that have a track record of delivering positive outcomes. Demonstrating impact can be a persuasive factor in securing funding.
- Engaging Stakeholders: Effective communication of outcomes engages stakeholders, including patients, healthcare professionals, and the community. It reinforces trust and fosters continued support.
Strategies for Showcasing Impact and Outcomes:
- Define Clear Objectives and Metrics:
- From the outset, establish clear and measurable objectives for your healthcare initiative. Define the metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to evaluate success.
- Collect Comprehensive Data:
- Rigorously collect data throughout the project or initiative. This should include baseline data, progress data, and final outcomes.
- Ensure data collection methods are accurate and consistent.
- Quantify and Qualify Results:
- Quantify the results by presenting data in numerical terms. For example, highlight the percentage reduction in a specific health condition, the number of patients served, or the increase in healthcare access.
- Complement quantitative data with qualitative insights, including testimonials, patient stories, and feedback from healthcare professionals.
- Use Visualizations:
- Create visual representations of data, such as graphs, charts, and infographics. Visuals make complex information more accessible and engaging for a wider audience.
- Tell Compelling Stories:
- Craft narratives that highlight real-life examples of individuals or communities positively impacted by your healthcare initiatives.
- Share success stories that illustrate the tangible benefits of your work.
- Demonstrate Cost-Effectiveness:
- Provide evidence of the cost-effectiveness of your initiatives. Compare the outcomes achieved to the resources invested to showcase efficiency.
- Benchmark Against Industry Standards:
- Compare your outcomes to industry or healthcare sector standards and benchmarks. This context helps stakeholders understand the relative success of your initiatives.
- Engage in Continuous Improvement:
- Showcase your commitment to ongoing improvement. Discuss how you have learned from past outcomes and adjusted your strategies accordingly.
- Engage Stakeholders Actively:
- Involve stakeholders in the process of evaluating and showcasing outcomes. Seek their input and insights to build a comprehensive picture of impact.
- Use Multiple Communication Channels:
- Disseminate your outcomes through a variety of channels, including reports, presentations, websites, social media, and newsletters. Tailor your message to suit each platform.
- Seek Third-Party Validation:
- Collaborate with independent evaluators or research institutions to validate your outcomes and findings. External validation adds credibility.
- Sustain Engagement:
- Maintain engagement with stakeholders even after the project is completed. Continue to share updates and long-term impact assessments.
Gathering Necessary Documentation: The Key to Successful Healthcare Initiatives
Effective healthcare initiatives require careful planning, execution, and documentation. Gathering the necessary documentation is a crucial step in ensuring the success and sustainability of healthcare projects, whether you’re a healthcare organization, researcher, or an individual seeking support for your healthcare endeavor. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the importance of gathering necessary documentation and provide insights into the process.
The Importance of Gathering Necessary Documentation:
- Compliance and Accountability: Documentation ensures that your healthcare initiatives comply with regulatory requirements and guidelines. It also establishes a clear record of how resources are used.
- Transparency: Documentation fosters transparency and trust among stakeholders, including funders, partners, and the community. It demonstrates a commitment to openness and accountability.
- Evaluation and Improvement: Comprehensive documentation allows for the evaluation of the initiative’s progress and outcomes. It provides insights into what is working well and where improvements can be made.
Essential Documentation for Healthcare Initiatives:
- Project Proposal:
- The initial project proposal outlines the objectives, scope, and goals of the healthcare initiative. It serves as a blueprint for the project.
- Budget and Financial Records:
- Maintain detailed financial records, including budgets, invoices, receipts, and expense reports. These documents track the allocation of funds and ensure financial transparency.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
- Keep copies of permits, licenses, and any legal documentation required for the healthcare initiative, such as institutional review board (IRB) approvals for research projects.
- Contracts and Agreements:
- If there are contracts or agreements with partners, vendors, or collaborators, retain copies of these documents. They define roles, responsibilities, and expectations.
- Progress Reports:
- Regular progress reports provide an overview of the initiative’s accomplishments, challenges, and milestones. They are vital for ongoing evaluation and communication with stakeholders.
- Patient or Participant Records:
- For healthcare initiatives involving patients or participants, maintain confidential and secure records in compliance with relevant privacy laws and regulations.
- Research and Data Collection:
- If your initiative includes research, document the research design, methodologies, data collection tools, and data sets. This documentation is essential for research validity and replication.
- Communication Records:
- Keep records of all communication related to the healthcare initiative, including emails, letters, meeting minutes, and reports. These records provide historical context.
- Evaluation and Assessment Tools:
- Document the tools and metrics used for evaluating the impact and outcomes of your healthcare initiative. This includes surveys, questionnaires, and assessment criteria.
Strategies for Effective Documentation:
- Create a Central Repository:
- Establish a secure and organized central repository or digital system for storing all documentation related to the healthcare initiative. Ensure that authorized team members have access.
- Use Standardized Forms:
- Utilize standardized forms and templates for documenting various aspects of the initiative, such as progress reports, patient records, and financial records.
- Implement Version Control:
- Implement version control for important documents to track revisions and updates. This prevents confusion and ensures that stakeholders are working with the most current information.
- Train Team Members:
- Train team members and staff on the importance of documentation and best practices for record-keeping. Encourage consistency in documenting processes and activities.
- Regularly Update Records:
- Maintain a routine schedule for updating records and documentation. Regular updates ensure that information is accurate and up to date.
- Backup Data:
- Regularly backup digital documentation to prevent data loss due to technical failures or unforeseen circumstances.
- Secure Confidential Information:
- Safeguard confidential or sensitive information, such as patient data, in compliance with applicable privacy laws and regulations.
- Plan for Long-Term Storage:
- For initiatives with long-term impact, plan for the secure storage and accessibility of documentation beyond the project’s duration.
Medical Documentation: The Backbone of Effective Healthcare
In the realm of healthcare, the importance of meticulous medical documentation cannot be overstated. Whether you’re a healthcare provider, researcher, or patient, comprehensive and accurate medical records play a pivotal role in ensuring quality care, treatment efficacy, and overall healthcare management. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the significance of medical documentation and provide actionable insights into its management and importance.
The Significance of Medical Documentation:
- Patient Care and Safety:
- Medical records serve as a comprehensive source of information about a patient’s medical history, conditions, treatments, and medications. This information is crucial for informed decision-making and ensuring patient safety.
- Continuity of Care:
- Accurate medical documentation facilitates continuity of care. When multiple healthcare providers are involved in a patient’s treatment, thorough records ensure that everyone is on the same page regarding diagnosis and treatment plans.
- Legal and Ethical Compliance:
- Healthcare providers are legally and ethically bound to maintain medical records. Proper documentation ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and ethical standards.
Essential Elements of Medical Documentation:
- Patient Information:
- Comprehensive patient information includes personal details, medical history, contact information, and insurance details.
- Medical History:
- Detailed medical histories encompass information about past illnesses, surgeries, medications, allergies, and family medical history.
- Assessment and Diagnosis:
- Clear and precise assessment and diagnosis records document a patient’s current condition and provide the basis for treatment decisions.
- Treatment Plans:
- Treatment plans outline the course of action, including medications, therapies, surgeries, and other interventions. They include details about dosage, frequency, and duration.
- Progress Notes:
- Progress notes document a patient’s ongoing condition, response to treatment, and any changes in diagnosis or treatment plans.
- Medication Records:
- Accurate records of medications, including name, dosage, administration route, and frequency, are vital to prevent medication errors.
- Laboratory and Test Results:
- Laboratory reports, imaging results, and test findings provide valuable diagnostic and monitoring information.
- Consent Forms:
- Consent forms, signed by patients or their legal representatives, are essential for procedures, surgeries, and treatments.
Strategies for Effective Medical Documentation:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs):
- Embrace electronic health record systems to streamline documentation, improve accessibility, and reduce the risk of errors.
- Standardized Terminology:
- Use standardized medical terminology and coding systems, such as SNOMED CT or ICD-10, to enhance clarity and interoperability.
- Timely Documentation:
- Document patient encounters and procedures promptly to ensure that information is current and accurate.
- Legibility and Clarity:
- Maintain legible and clear documentation to prevent misinterpretation and errors. Use blue or black ink when documenting by hand.
- Privacy and Security:
- Safeguard patient information to ensure privacy and security in compliance with healthcare data protection laws and regulations.
- Consistency and Completeness:
- Ensure that medical records are complete and consistent. Avoid leaving gaps or missing information.
- Cross-Referencing:
- Cross-reference information when necessary to connect related records and provide context.
- Training and Education:
- Healthcare providers and staff should receive training on proper documentation practices and stay updated on regulatory requirements.
Letters of Recommendation: Navigating the Art of Professional Endorsement
Letters of recommendation are powerful endorsements that shed light on an individual’s qualifications, character, and capabilities. Whether you’re applying for a job, seeking admission to an educational institution, or vying for a prestigious opportunity, well-crafted letters of recommendation can make a substantial difference. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the significance of letters of recommendation and provide actionable insights into their composition and importance.
The Importance of Letters of Recommendation:
- Objective Validation:
- Letters of recommendation provide an objective evaluation of an individual’s skills, experience, and suitability for a particular role or program.
- Highlighting Strengths:
- They offer a platform to emphasize a candidate’s strengths, achievements, and qualities that may not be apparent from a resume or application.
- Trust and Credibility:
- Letters of recommendation are trusted sources of information about an individual’s professional and personal attributes. They enhance credibility in competitive scenarios.
Essential Elements of Letters of Recommendation:
- Introduction:
- Begin with a formal salutation and an introduction that identifies the recommender and their association with the candidate.
- Context and Relationship:
- Describe the context of the relationship between the recommender and the candidate. Explain how long they have known each other and in what capacity.
- Specific Qualities and Achievements:
- Detail the candidate’s specific qualities, skills, and achievements. Provide examples and anecdotes that illustrate their capabilities.
- Comparative Statements:
- Compare the candidate to their peers or colleagues to emphasize their exceptional qualities or contributions.
- Relevance to the Role or Program:
- Highlight how the candidate’s qualifications align with the requirements of the role or program they are applying for.
- Personal Attributes:
- Discuss the candidate’s personal attributes, such as work ethic, integrity, leadership, and teamwork skills.
- Conclusion:
- Conclude with a strong endorsement and an invitation for further contact if needed.
Strategies for Effective Letters of Recommendation:
- Selecting Recommenders:
- Choose individuals who are well-acquainted with your work and character. They should be able to provide specific and meaningful insights.
- Customization:
- Tailor each letter of recommendation to the specific role, program, or opportunity you are applying for. Generic letters lack impact.
- Provide Supporting Materials:
- Offer your recommender a copy of your resume, transcripts, or other relevant documents to aid them in composing a comprehensive letter.
- Give Ample Notice:
- Request letters of recommendation well in advance of deadlines to allow recommenders adequate time to write thoughtful and well-crafted letters.
- Follow Up:
- Politely follow up with recommenders to ensure they meet deadlines and offer assistance if needed.
- Professional Formatting:
- Ensure that the letter is professionally formatted, including appropriate fonts, margins, and spacing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Generic Letters:
- Avoid using generic, one-size-fits-all letters of recommendation. They lack authenticity and depth.
- Overly Brief or Vague Content:
- Letters that are too short or lack specific details do not provide a compelling endorsement.
- Ignoring Guidelines:
- Pay attention to any specific guidelines or requirements provided by the recipient of the letter, such as word limits or formatting preferences.
Exploring Alternative Funding Options: Beyond Traditional Sources
In the pursuit of personal or business goals, funding is often a critical factor that can determine success or stagnation. While traditional sources like banks and investors are common choices, alternative funding options have gained popularity for their flexibility and accessibility. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of alternative funding, explore various options, and shed light on how they can be leveraged to fuel your ambitions.
Understanding Alternative Funding:
- Diverse Sources:
- Alternative funding encompasses a wide range of non-traditional sources, including crowdfunding, peer-to-peer lending, grants, and more.
- Accessibility:
- Many alternative funding options are more accessible to individuals, startups, and small businesses than traditional financing methods.
- Flexibility:
- Alternative funding offers flexibility in terms of the types of projects or initiatives that can be funded and the terms of repayment.
Types of Alternative Funding Options:
- Crowdfunding:
- Crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo allow individuals and businesses to raise funds from a large pool of contributors. Rewards-based and equity crowdfunding are common models.
- Peer-to-Peer Lending:
- P2P lending platforms connect borrowers with individual lenders, often offering competitive interest rates and streamlined application processes.
- Angel Investors:
- Angel investors are individuals who provide capital to startups or early-stage businesses in exchange for equity ownership.
- Venture Capital:
- Venture capital firms invest in startups with high growth potential in exchange for equity. They often provide mentorship and expertise.
- Grants:
- Grants are non-repayable funds provided by governments, foundations, and organizations to support specific projects or initiatives.
- Bootstrapping:
- Bootstrapping involves self-funding your venture using personal savings or revenue generated by the business itself.
Strategies for Leveraging Alternative Funding:
- Research and Preparation:
- Thoroughly research and identify the most suitable alternative funding option for your project. Prepare a compelling proposal or campaign.
- Diversify Sources:
- Consider diversifying your funding sources to reduce risk. Combining crowdfunding, grants, and personal savings, for example, can provide stability.
- Network and Pitch:
- Build relationships with potential investors or donors. Attend networking events, pitch your ideas, and demonstrate passion and commitment.
- Transparent Communication:
- Maintain transparent communication with your funders or backers. Keep them informed of progress and challenges.
- Use Online Platforms:
- Leverage online platforms and social media to reach a broader audience for crowdfunding campaigns.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid:
- Neglecting Due Diligence:
- Conduct thorough due diligence when selecting alternative funding sources or partners to avoid potential scams or unreliable options.
- Underestimating Costs:
- Accurately estimate the costs associated with your project to avoid falling short of funds mid-way.
- Overpromising Rewards:
- In crowdfunding campaigns, avoid overpromising rewards that may be difficult to fulfill, leading to disappointment among backers.
Conclusion:
Medical grants are more than just financial support; they are lifelines that bridge the gap between healthcare needs and available resources. Throughout this exploration of medical grants, we have uncovered their profound importance, the various providers, the critical eligibility criteria, and the essential application processes.
Medical grants offer hope to patients seeking life-saving treatments, enable healthcare professionals to push the boundaries of medical research, and empower communities to build healthier futures. They are a testament to the collective commitment to ensuring access to quality healthcare for all.
Whether these grants come from government entities, private foundations, or community-based initiatives, their impact is undeniable. They inspire innovation, drive advancements in medical science, and, most importantly, improve the lives of individuals facing health challenges.
As we navigate the complexities of the healthcare system, we must remember that medical grants are not just financial support; they are a beacon of hope and a symbol of compassion. They remind us that together, we can make a difference in the lives of those who need it most. So, whether you are a grant seeker, a healthcare provider, or a member of the community, let us continue to work collectively to harness the power of medical grants for the betterment of healthcare worldwide.
Essential Reads for Grant Writing Excellence
Grants can unlock vast potentials, but securing them? That’s an art and a science. Whether you’re new to the field or looking to enhance your skills, these hand-picked titles will elevate your grant-writing game:
Go Beyond Basics: Dive into strategies and techniques that make proposals irresistible. With insights into a reviewer’s mindset, stand out and shine even in fierce competition.
Be Grant-Ready: Ensure your organization isn’t just applying but is truly ready to manage and utilize grants. Streamline, assess, and position yourself for success from the get-go.
From Novice to Pro: Covering the entire spectrum of grant writing, this guide offers invaluable tips, examples, etc.. It’s your blueprint to mastering the craft.
4. The Small Business Guide to Winning Grants:
Business-Specific Brilliance: Designed for small businesses, navigate the unique challenges you face. Find, apply, and win grants tailored just for you.
Think, Act, Succeed: More than writing – it’s about strategy and mindset. Step into the shoes of a guru, understand funder desires, and become indispensable in the grant world.
Why These Titles?
Securing grants isn’t just about paperwork; it’s about alignment, narrative, and persuasion. The above titles are your arsenal in this endeavor, carefully crafted to offer actionable insights for every level of expertise.
In a realm where competition is stiff, your edge lies in continuous learning and adaptation.
Grab these books, absorb their wisdom, and position yourself as the top contender in the grant game. Your journey to becoming a grant virtuoso begins with these pages. Dive in!
Unlock Your Grant Success!
Join our email list now for exclusive grant-writing tips and unique grant opportunities delivered straight to your inbox. Click here to Subscribe. Don’t miss out!
Invitation: Exclusive Live Workshop on Grant Writing in Abuja
We are excited to extend an exclusive invitation to you for our upcoming Live Workshop on Grant Writing, scheduled to be held in the heart of Abuja by the end of November. This is a golden opportunity for individuals and organizations aiming to sharpen their grant-writing skills, gain in-depth insights into the world of grant-making, and increase their chances of securing essential funding.
Event Details:
- Date: 27th November, 2023 – 1st December, 2023
- Time: 9:00 AM – 3:00 PM
- Venue: Abuja, Nigeria
Why Attend?
- Expert-Led Sessions: Our panel consists of renowned grant-writing professionals with a track record of securing millions in funds for diverse projects.
- Hands-On Training: Dive deep into real-world grant applications, understand the do’s and don’ts, and refine your approach with practical exercises.
- Networking Opportunities: Rub shoulders with fellow grant writers, and potential collaborators.
- Comprehensive Material: Every participant will receive a curated grant-writing toolkit, complete with templates, sample applications, and a list of potential grantors.
Workshop Highlights:
- Foundation of Grant Writing: Learn the fundamental principles that set apart winning proposals from the rest.
- Narrative Crafting: Uncover the art of storytelling in grant applications, ensuring your project stands out and resonates with funders.
- Budgeting & Financial Projections: Understand how to create a robust and transparent financial plan that instills confidence in potential grantors.
- Tailoring Applications: Every funder is unique. Gain insights into tailoring your applications to resonate with specific grantors’ missions and values.
- Feedback & Reviews: Get your past or draft applications reviewed by experts, garner constructive feedback, and learn ways to enhance them.
Registration Details:
- Early Bird Fee: N350,000 (Includes workshop materials, lunch, and a certificate of participation.)
- Early Bird Offer: Register by November 10th and avail a 10% discount!
- How to Register: Visit https://selar.co/873716 or call us at +2348111442950 or email at grantwritingacademy@gmail.com.
- Late Registration Fee: N500,000
- Note: Seats are limited, and registrations will be on a first-come, first-served basis. So, hurry and secure your spot today!

Join Us & Transform Your Grant Writing Journey!
The world of grant-making is competitive, but with the right skills and approach, you can significantly increase your chances of success. Whether you’re a beginner stepping into the realm of grant writing or a seasoned professional looking for advanced strategies, this workshop promises value at every level.
Abuja, with its vibrant community of NGOs, startups, and institutions, is the perfect backdrop for this transformative event.
So, mark your calendars, spread the word, and gear up for a day of learning, networking, and empowerment!
We eagerly look forward to welcoming you and embarking on this enriching journey together.